Cadmium telluride
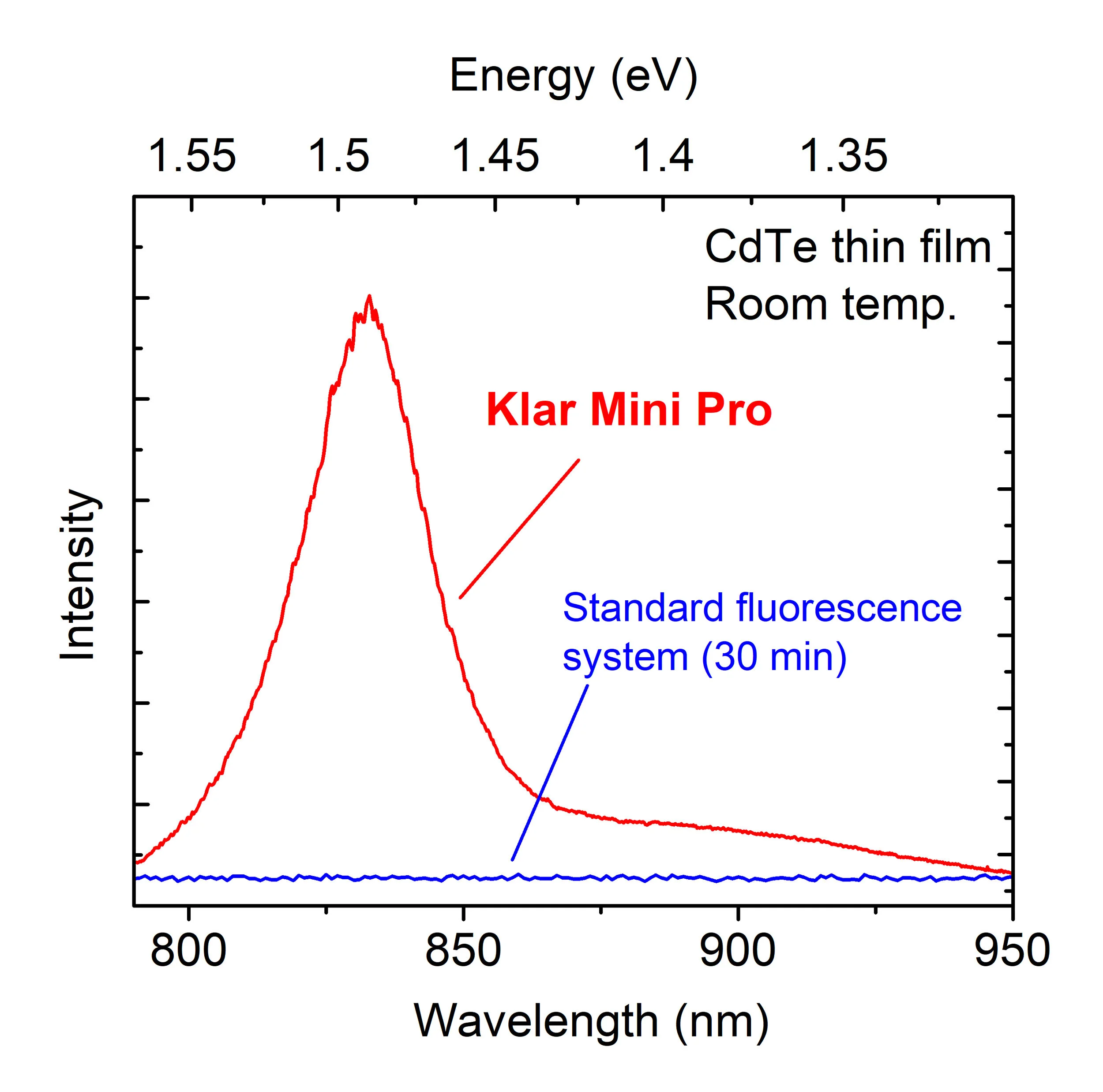
Cadmium telluride (CdTe) and cadmium zinc telluride (CdZnTe, or CZT) are semiconductors with applications in solar cells and particle detection. For the solar cell market, low-cost synthesis techniques must be developed. An example of a PL spectrum of a CdTe thin film is shown in the figure. Because the film is rough, the emitted light is scattered, making detection difficult. A standard (non-microscope) fluorescence system was unable to obtain a signal. The Klar microscope, in contrast, collected emitted photons efficiently and produced a high-quality spectrum.
To evaluate the composition across a bulk CZT crystal, a PL scan was performed over a large area. Using a rapid peak-fitting routine, the PL energy was plotted in a false-color image. The PL energy provides a measure of the band gap, which increases with Zn content, and hence composition. The PL map clearly shows variation of composition along the growth axis of the crystal. Focus was maintained even though the sample was fragmented.
False-color image of the PL peak energy in a slice from a CdZnTe boule.